3 Tier Architecture vs Hyper Converged Infrastructure
The Primary Differences Between a 3-Tier Architecture vs a Hyper Converged Infrastructure
Explore the pros and cons of 3-tier architecture and hyper converged infrastructure with Fortuna Data. Find the perfect data storage solution for your business needs.
Many organisations have pools of storage on premise and in the cloud and this takes many forms File, Block, Object, DAS, SAN, NAS, Buckets. Whilst many organisations are preferring to use the cloud for their off-premise storage there are many organisations now looking at being “Cloud Smart”. They have realised that there are many use cases where the cloud is no longer suitable or too costly to store data for long periods of time.
In this article we look at two competing types of storage technologies that are completely different in how they are architected and more importantly how they function and operate.
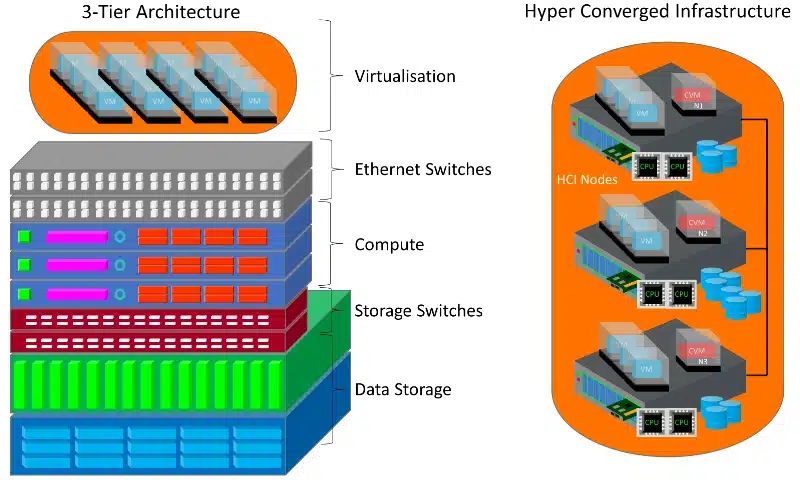
3-Tier Architecture
The first is a traditional 3-tier architecture comprising of servers, storage, networking, and a software hypervisor.
Advantages of a 3-Tier Architecture:
- Modularity and Scalability: Each tier has a distinct role, making it easier to modify individual components for future upgrades. You can scale each tier independently based on the specific needs of your application. For example, you can add more servers or storage to handle increased data or compute.
- Enhanced Performance: With a 3-tier architecture, each tier can be optimised independently to maximise performance. The presentation layer focuses on delivering an intuitive user interface, while the application layer handles complex processing tasks efficiently. Meanwhile, the data layer ensures quick retrieval and storage of information. This division of responsibilities prevents bottlenecks and optimises overall system performance.
- Ease of Maintenance: In a 3-tier architecture setup, maintenance becomes more manageable due to clear separation between components. Developers can make changes or updates within specific layers without impacting others’ functionalities significantly. Additionally, when troubleshooting issues arise, pinpointing problem areas becomes simpler since they are compartmentalised into separate tiers.
- Cost-Effective Infrastructure Scaling: A 3-tiered approach enables organisations to optimise their infrastructure costs by scaling only the necessary layers based on demand patterns rather than scaling everything together as in monolithic architectures. This targeted scalability minimises resource wastage while catering precisely to the specific needs of each layer.
Disadvantages of a 3-Tier Architecture:
While the 3-tier architecture offers numerous advantages, it is not without its downsides. One of the main disadvantages is increased complexity. With three layers – presentation, application, and data storage – there are more components to manage and maintain.
- Complexity: Increased complexity: Implementing and managing a multi-tier architecture can be more complex than a single-tier architecture, particularly for smaller applications with limited requirements.
- Latency: Increased network latency: Communication between tiers over a network can introduce latency, which may impact the performance of real-time or highly responsive applications.
- Cost: Infrastructure costs: Maintaining separate servers or resources for each tier can lead to increased infrastructure costs, especially if you need to scale horizontally.
- Overhead: Increased overhead: Inter-tier communication, data serialisation, and network traffic can add overhead to the application, affecting performance.
- Development Time: Longer development time: Designing and implementing a three-tier architecture may require more time and effort compared to a simpler, single-tier architecture.
- Potential for Bottlenecks: Bottlenecks: Inefficient design or resource allocation can lead to bottlenecks in the application, where one tier becomes a performance bottleneck for the entire system.
- Over provisioning: When designing a 3-tier architecture is often the case that an organisation will purchase more powerful processors or memory to accommodate predicted future growth.
- Management Complexity: Having a 3-tier architecture is more complex to manage as IT staff need to have skills in managing networking, server configurations, hypervisor, and storage management. This adds to the complexity of the solution, costs, and increased overheads.
- Vendor tie in: Investing a 3-tier solution normally involves single manufacture making it difficult to change vendors in the future.
- Troubleshooting: Additionally, troubleshooting and debugging can become more complex in a 3-tier architecture due to the distributed nature of components. Identifying issues may require analysis across multiple tiers, making it imperative for teams to have strong monitoring tools and practices in place.
- Security: Security is also a major consideration when dealing with a 3-tier architecture. With multiple layers involved, each requiring its own security measures, organisations must implement robust security protocols at every level – from securing network connections to protecting sensitive data stored in databases.
- Fixed use case: A 3-tier solution is designed to provide either file or block storage making it inflexible for future organisational requirements.
- Operational costs: A 3-tier architecture will consume more energy as there are more system components required.
3-tier Summary
A three-tier architecture offers many benefits in terms of modularity, scalability, and maintainability. However, it also comes with added complexity, potential performance overhead, and increased infrastructure costs. The choice of whether to use a three-tier architecture should be based on the specific requirements and goals of the organisation.
Hyper Converged Infrastructure
The second is a hyper converged infrastructure (HCI) running a software layer on top of servers to provide file, block, object storage and/or a hypervisor and managed as a cluster.
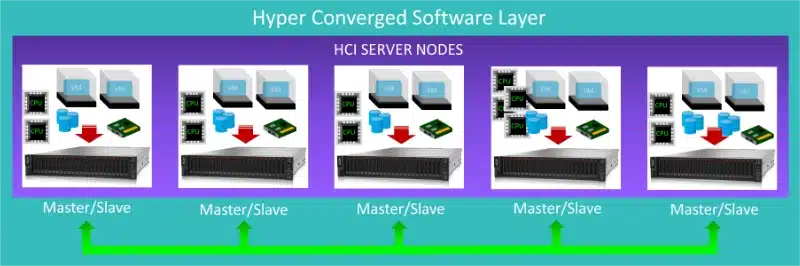
Advantages of a Hyper Converged Infrastructure:
- Simplified Management: Hyper Converged Infrastructure solutions offer a unified management interface, making it easier to deploy, configure, and manage the entire infrastructure stack from a pane of glass or GUI.
- Scalability: HCI allows for granular scaling by adding nodes for additional storage, compute, or GPU’s, making it straightforward to expand resources as your organisation’s needs grow.
- Cost Efficiency: HCI can reduce hardware and operational costs by consolidating resources and optimising utilisation, leading to a lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Improved Performance: HCI solutions use a clustered architecture enabling the aggregation of available resources providing higher performance access to data and applications.
- Simplified Reporting & Management: Unlike a 3-tier solution HCI manages and controls all aspects of the environment with a wizard driven interface, changes can be made with the minimum of user intervention and advanced reporting can easily show where resources are being utilised and consumed.
- Rapid Deployment: HCI solutions are designed for quick deployment, reducing the time it takes to get new infrastructure up and running.
- Security Hardened: HCI is more secure than a 3-tier solution as it is security ready out of the box. It handles all the patches and updates automatically and takes each node offline until all the updates have been performed.
- Disaster Recovery: HCI solutions incorporate data protection features like snapshots, replication, and backup, simplifying disaster recovery planning.
- Operational Simplicity: By investing in an HCI solution enables organisations to do more for less, i.e., less training, less complexity, greater flexibility to provide additional functionality such as VDI.
- Flexibility: HCI provides many additional benefits over 3-tiered solutions as they are like a Swiss army knife. Some provide a built-in hypervisor making it well suited for virtualisation, need file, block, or object storage HCI can also accommodate this as well as many other use cases.
- Cloud Elasticity: HCI enables businesses to run applications on premise and move them to the cloud when demand arises allowing organisations to control cloud spend.
Disadvantages of Hyper-Converged Infrastructure:
- Initial Cost: The initial investment in HCI hardware and software can be higher compared to traditional infrastructure solutions, which might be a barrier for some organisations.
- Limited Customisation: While Hyper Converged Infrastructure offers simplicity, it may not provide the same level of customisation and fine-tuning as traditional infrastructure solutions for specific use cases.
- Resource Contention: In some cases, multiple workloads running on the same HCI cluster may compete for resources, which can affect performance if not managed properly.
- Complexity at Scale: Managing and scaling large HCI deployments can become complex, requiring careful planning and expertise.
- Data Sovereignty: Data residency and compliance concerns may arise when using HCI solutions, especially if data must remain in specific geographic locations.
- Learning Curve: HCI may require IT staff to acquire new skills and adapt to a different operational model, especially if they are accustomed to traditional infrastructure.
HCI Summary
In summary, HCI offers advantages such as simplified management, scalability, cost efficiency, and performance improvements. However, organisations should carefully consider the initial costs, potential vendor lock-in, and the suitability of HCI for their specific workloads and requirements before adopting this infrastructure approach.
Why bother writing this?
I have been working with a billion-pound turnover organisation who have traditionally purchased a 3-tier solution and whilst this has served them, they want the flexibility to include other areas of the business where a 3-tier architecture wouldn’t work for example, ROBO (remote office branch office), Edge, DR, VDI). With less money being invested in IT and a reduced IT headcount HCI offers many advantages for example all systems can be managed centrally.
If you would like to know more about the 3-tier or HCI solutions we provide please contact us using the details below.